Introduction
Health service in Thai society today takes into account human rights and public opinion. Nurses are health service professionals who share responsibility for making this society healthy. Moreover, the development of nursing education and curriculum requires the opinion and guidance from stakeholders (ASEAN University Network, 2015). Boromarajonani College of Nursing Saraburi (BCNS) under the Praboromarajchanok Institute, Thai Ministry of Public Health is responsible for providing nursing education in the central region of Thailand. The main mission of BCNS is to produce quality nurses through higher standards of education focusing on the production and development of the nursing workforce to work in health systems at all service levels. Although the previous results of the Evaluation of Graduate Quality According to Thai Qualifications Framework for Higher Education (Ministry of Education, 2006) overall was at the very good level = 4.30, S.D. = .47), with the utmost awareness of the users, in the age of social change, the BCNS has systematically studied the needs of the stakeholders, which will lead to the improvement of the curriculum to make it up-to-date and the most effective for serving patients. The curriculum was based on humanized nursing care which provides total care to the patients according to the four dimensions of health; physical, social, mental, and spiritual. This curriculum aims to encourage a service-oriented mindset, teaches assertiveness, innovation and brings moral value to society. Moreover, quality assurance in teaching and learning management from the admissions by academic staff, teaching and learning management, learning support, and infrastructure from the stakeholder perspective were important to set fundamentals for further education and professional nursing development (Todres et al., 2009; Wangthong et al., 2013).
Research Objectives
-
To study the desired characteristics of the nursing school graduates as perceived by the stakeholders.
-
To study the factors concerning nursing curriculum development as perceived by the stakeholders.
Method
The Population and Sample
The stakeholders in this study were comprised of a group of persons who are involved in the process of graduate production of BCNS, which includes 1) alumni 2) supervisors and colleagues of the alumni 3) nursing lecturers and 4) current students. Different sampling methods were used to draw the key informants from each group in this study.
The alumni. The process began by selecting alumni who had graduated during the years 2012-2016. Quota sampling was used to determine the sample size selected to represent the alumni who are working in different geographic regions throughout the country; at least 2 alumni from each geographical region were selected
The supervisors and colleagues of the alumni. The sample size of this group is determined based on the number of alumni, which included 11 key informants. The snowball technique (Nissim & Tamar, 2011) was used to draw the sample to represent this group.
The nursing lecturers. This group was drawn from the nursing lecturers who were currently working at BCNS at time of data collection. One lecturer was drawn from each of five departments (Nursing mothers, newborn and midwifery nursing; mental health and psychiatry nursing; community health nursing; gerontology nursing; and child and adolescent nursing). An invitation letter was sent to lecturers in each department asking for a volunteer to participate in an in-depth interview.
The current nursing students. Two students from each level (1st to 4th year students), were drawn by convenient sampling on their voluntary basis.
Ethical Considerations
The approval to conduct research was obtained from the BCNS ethical committee. Volunteers were asked to participate in the research and could leave the study any time they wanted.
Research Instrument
An interview guide was used to guide the interviewing sessions. The two main questions were:
Data Collection and Analysis
The in-depth interview and focus group discussion were used to collect the data from 55 key informants as detailed in Table 1.
Two focus group interviews were conducted among the supervisors and colleagues and the current nursing students group. In-depth interviews were conducted to collect data from the alumni and the nursing lecturers group, Focus group interviews lasted around 2 hours for each session. A probing technique was used to encourage the key informants’ conversation and flow of ideas concerning the topic. Each in-depth interview lasted between 45 minutes to one and a half hours. Data collection was conducted during the first semester of the 2017 academic year.
The interviews were tape-recorded and transcribed verbatim. The transcription of the interview data was content analyzed and data triangulation was used to validate the research data. The results were presented in two sections: desired characteristics of nursing school graduates and factors concerning the nursing curriculum development.
Results
I. Desired Characteristics of Nursing School Graduates
Future nursing graduates should have four main characteristics: knowledge, skills, morals and professionals ethics, and nursing competency (Figure 1). The stakeholders reflected on the future nursing graduates’ characteristics as follows.
Knowledge Domain
In the future, nurses must have knowledge related to basic knowledge; a specialty area; nurse roles in prevention, promotion, cure, and rehabilitation; essential knowledge to pass the license exam for registered nurses; emerging infectious diseases; global changes; and health system laws regarding the nursing profession;. Below are selected quotations of key informants that describe their views on knowledge that nursing graduates should have.
Basic knowledge is the root for development and advancement in deeper and specialty nursing. Key informants stated that:
“Nursing knowledge must be accurate, so the nurses can develop more advanced levels of knowledge.”
“…knowledge promotes confidence in careers,…able to coach and supervise their team member”
“… smart nurse with good basic nurse knowledge, was recognized by others.”
“…have firm basic knowledge, before developing characteristics of future nurses.”
Knowledge in specialty areas was important for working as a nurse with a specialty. An informant described it thusly: 
“…have qualified knowledge and can apply it in nursing specialty areas.”
Knowledge in four major roles of nurses in health promotion, disease prevention, treatment, and health restoration were discussed. An informant described as:
“…have basic knowledge to perform four major responsivities of a nurse: promotion, prevention, care, and rehabilitation.”
Passing of the professional license test was reported asa criterion to meet the standard. Key informants said: 
“…should have knowledge for passing registration professional licensing test.”
“..can meet the qualification of the knowledge and skills test.”
Laws concerning the nursing profession are important; several issues were discussed. Key informants pointed to: 
“…knowledge of the Constitutional Law, Professional Law Act, Public Health Economics, Health science with emphasis on new subjects, mass psychology, and knowledge of nutrition.”
“…knew the law of self-employment.”
Emerging infectious disease knowledge was included as important knowledge for nursing school graduates to have. They said:
“…need to know about the disease that will come with the AEC and more open to nursing migration among AEC countries.”
Global change was identified in the area of the changing world and technology. A key informant stated that it:
“…new knowledge must be understood, according to global changes, new technology, and information”
Health systems were specified as patient safety culture and safety organization. An informant stated that nurses: 
“… should know the 12 elements of health systems that are considered part of safety culture, making their organization have a safety culture.”
Skills Domain
Skills were divided into 3 types: lifelong learning, critical thinking, and communication skills.
Lifelong learning was suggested as an important skill, since knowledge in health and nursing must continue to advance to improve patient outcomes. Nurses must have lifelong learning skills to update their knowledge. Lifelong learning is comprised of self-directed learning, self-development, learning about new things/events, new knowledge searching, and book reading. Key informants explained these as:
Self-directed learning Self-directed learning was described as “…having self-directed learning skills both working and personal matters.”
Self-development was referred to as
" …self-development by continuing education and learning more."
“…learn to develop yourself consistently; know your strengths and weaknesses. I knew how mistakes were made in my work, so I can improve and make no more mistakes.”
“Good nurses are responsible, active self-learners for self-development.”
Learning new things/events. Informants commented that nurses
“…should seek to know and find new methods or innovation for self - challenges.”
“…should be persons who search to learn any time they meet a new thing, must learn new knowledge to build on previous knowledge. Knowledge makes a person keen to share ideas.”
New knowledge searching is a must as nurses must be learners, studying and researching continuously to be experts. Some suggested that nurses should 
“…be enthusiastic and knowledge seeking.”
“…be a person who is always searching for knowledge”
“…have contemporary contextual learning skills.”
“…should search for new knowledge all the time; it does not end at graduation.”
“…have skills for new knowledge seeking, learning and adapting to new knowledge requires a professional background. When we have the knowledge, we will be smart. If we do not learn new knowledge, we will be only waiting for other orders.”
Reading book was mentioned as*“…pursuit knowledge and learning, reading led to essential news of society and political changes.” *
Critical thinking
Critical thinking was comprised of holistic problem solving and decision-making. Respondents further explained their opinion that critical thinking is an important characteristic of nurses as follows:
Communication
Communication was described as important knowledge while delivering nursing care. Future nurses will require more knowledge to communicate confidently and competently with clients and a multidisciplinary team. These will reduce the risks of prosecution and be secure at their workplace. Key informants reflected on this issue as:
“…some bad words caused prosecution. Nurses must be careful and respond every time the patient requests [something] which will bring [patients] a feeling that they are being taken good care of.”
“The ability to practice and communicate while working as nurses.”
“Nurses must communicate with clients with common words and avoid technical terms, because patients do not ask questions when they don’t understand.”
Moral and Professional Ethics Domain
The morals of nurses are embedded in service behavior and divided into personal morals and nursing professional ethics.
Personal morals
Personal morals are comprised of being a gentle, good person, showing mercy, being trusted, and being unselfish. They are further discussed as:
Nurses “…must be gentle with patients but not weak; reasonable and positive attitude.”
“…The first thing is being a good person, later being a good nurse.”
“…being kind, showing mercy to mankind, having a service-oriented mindset and seeing the patient’s problems holistically.”
“…must be a kind person, recognize the value of people while understanding the way of life in the community. Misunderstanding community life will easily cause an argument between the nurse and patient. Understanding facilitates nurse and patient friendships.”
“…importantly, a nurse should be a trusted person, and be a model of honesty.”
“The students in the new modern era were less tolerant of hard work” and “… should organize activities that related to religion in order to reinforce mental strength, self-awareness, catching up with the fast changes of the world.”
Professional ethics
Professional ethics have five subgroups: positive thinking, job completion, loyalty to the profession, responsibility, and generosity. Informants identified these as follows:
Positive thinking was explained as
"…have good personality and maturity, smiling, positive thinking, sense of humor, happiness, did not show bad temper during serv
“…being healthy, role model of a happy person.”
Job completion was mentioned as
“…have knowledge, morals, compassion, integrity, honesty and responsibility.”
“…have mercy, be generous with clients, and devoted to more than only money.”
“…responsible, including being devoted and tolerant to complete the job.”
Loyalty to the profession was often mentioned as
“…wants to be a nurse, loves the nursing profession, being devoted to others.”
"…nurses must be proud of their profession"
“…faithful to self, to client, with disciplined service.”
Responsibility was mentioned as
“Responsibility is the first priority needed, with self, organization, and client.”
Generosity was defined as
“…to care for the patient with the generosity that nurses really wanted to.”
“…nurses must think positively, willing to care for the patients, understand and accept the different cultures”
Nursing Competency Domain
Analysis revealed seven nursing competencies that future nurses should possesses: thinking, research, teamwork, management, nursing practice skills, English proficiency and technology skills.
Thinking
Thinking systematically and evidence-based analysis are the logic for problem solving, which nurses must have. Key informants addressed this as follows:
“Nurses must have systematic thinking and analytical thinking.” “…have systematic and holistic thinking that led to quality job performance.”
“… thinks quickly, sensitive to new problems, and problem solves independently.”
“…can have systematic thinking and concise patient care in one page, do not stick too much to a general form.”
“…a new trend in nursing is to provide evidence-based care.”
Research
Research is a competency that nurses must have as this is the background of innovation and empirical development in their work. Informants stated that:
“Nurses need to have research competency to apply research results and knowledge management.”
“…can apply empirical evidence based (EBN) to develop innovations.”
“…many hospitals were motivated to research Routine to Research, R2R, which should instill the research process skills in order to systematically find answers, which will make research development easy at the workplace.”
“…have research knowledge that can run fundamental research on data collection, data analysis in order to develop science related to the nursing profession, co-research, or apply research results.”
Teamwork
Nurses need teamwork competency to work with a health team. Teamwork skills with people in other professions were recognized as part of the nursing job by nursing students and were specified as:
“Nurses must have teamwork skill.”
“…co-ordinate roles, apart from nursing work, must find strategies to co-work with doctors, pharmacists and other professionals.”
“…good teamwork skills, can bring the leader from the private sector in a local area to be a partner of the health center or hospital.”
“…can work as a team with others professionals, and love your profession.”
“… coordinating with multidisciplinary team members, such as physical therapists.”
“…be able to manage jobs at any different service area.”
“…focus on management skills with other professions.”
“…be able to manage nursing resources, finances, tools and materials.”
“… by the next 5 years, the chronic diseases will increase. Nursing care is part of family doctor team. Nurses will do more coordinating with multidisciplinary team members, such as doctors, physical therapists, and local organizations.”
“…have the ability to manage, show good performance, and work with a network.”
Management
Management competency related to finances, equipment, staff, and network within or outside the organization can bring maximum benefits. Key informants stated that:
“Nurses can administer the systematic management.”
“…can work with community health networks, and stakeholders.”
“… coordinating with multidisciplinary team members, such as physical therapists.”
“…be able to manage jobs at any different service area.”
“…focus on management skills with other professions.”
“…be able to manage nursing resources, finances, tools and materials.”
“… by the next 5 years, the chronic diseases will increase. Nursing care is part of family doctor team. Nurses will do more coordinating with multidisciplinary team members, such as doctors, physical therapists, and local organizations.”
“…have the ability to manage, show good performance, and work with a network.”
Nursing practice skills
Nursing practice skills are skills that nursing graduates needed to have in order to apply to work in some particular practical areas which could guarantee operational quality. Key informants identified nursing practice skills as:
“…be able to provide service at the primary, secondary, and tertiary levels of service by being capable of managing, supporting, and counseling patients.”
“… practical training in real situations.”
“…have more practical skills in nursing profession rather than focusing only academics.”
English skills
English proficiency is something that nurses should possess, since English communication is one of the international standards required. Key informants expressed their views as:
“…for foreign language (English and other), [graduates] at least should have better English competency than previous graduates.”
“…have communication skills, in particular English is necessary in the AEC [ASEAN Economic Community] Era.”
“…nursing students should be taught English skills from the first year continuously until the last year.”
“The nurse needs good language skills in consideration of the AEC. English is important as a second language.”
“Whether the patient is from any nation, for example, Japan, or tourists, they will have an English translator come with them when the clients come to service sites.”
“…as members of the Association [AEC], nurses need to have knowledge of languages and cultures of neighboring countries.”
“…focused more on the language, most public hospitals have English communication problems.”
“…create more of an atmosphere and environment in English, such as using English words on bathroom signs, places, and buildings.”
Technology skills
Technology skills will enhance nurses’ ability to use technology and promote effective work. Stakeholders addressed technology as an important key to nursing job development. Key informants thought that:
“…today, nurses are mostly good with technology skills; they should use them for research and work development…”
“…the ability to use IT to communicate and work.”
“…used IT/Smartphone for nurse work, such as problem solving…”
“…must have IT usable for communication and new knowledge.”
“…should have competency of the technology that can be used in the work (nursing) and communication technology.”
II. Nursing Curriculum Development
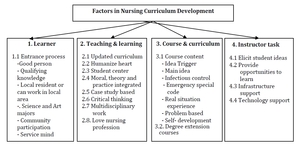
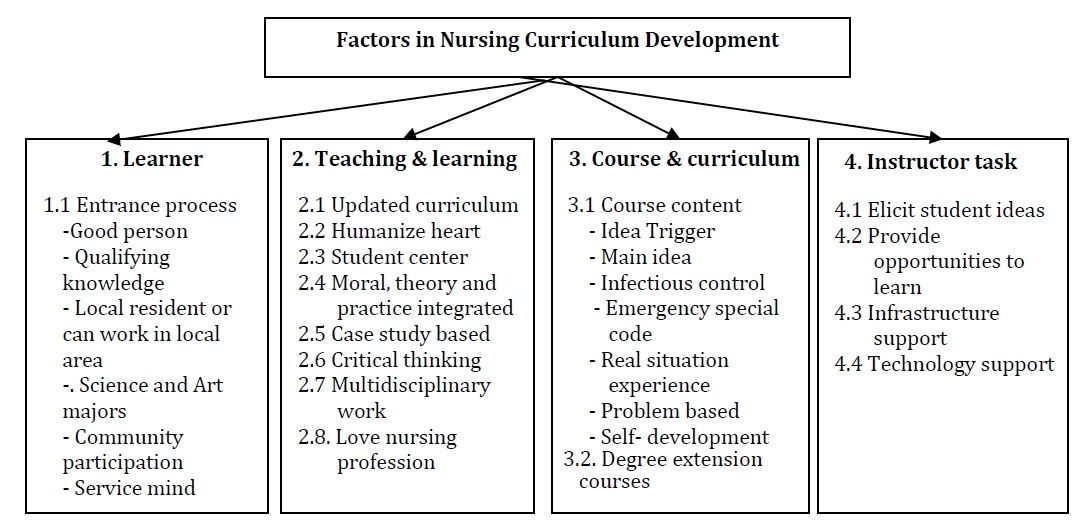
The stakeholders reflected on the factors concerning the development of nursing curriculum as shown in Figure 2 . It was composed of four elements: learner, teaching and learning, course and curriculum, and instructor tasks as follows.
Learner
Being a learner is a key factor of nursing performance, as well as quality of health care providers. The entrance process leads to the quality of the learner. Selection of people having good qualities for studying should consider the shortage of local nurses. Due to country development from a predominantly rural country to an increasingly urban one, most new nurses choose to work in the hospital rather than in the primary care setting. Selection should be based on local performance trends. Supervisors and colleagues of the alumni proposed the approach for the selection of nursing students as follows. The admissions criterion to select nursing students was divided into six parts: good person, qualifying knowledge, local resident, science or art major, community participation, and service mind. Selection criteria should focus on people with mercy and intellectual ability to get quality nurses.
A good person has qualities such as kindness, healthy mind, and mercy. Key informants suggested in selecting students that:
“…a kindness mindset, past mental assessment test prior to admission or as part of the selection process.”
“Good nurses must have good minds and mercy, not be materialistic. The nurse must be a person with a special type, other than general. Not all people can be a nurse.”
We should look for “…good people, people who want to study and live in the area, from community to community, rather than just focusing on their GPA.”
Qualifying knowledge refers to knowledge according to criteria set at admission, critical thinking, and aptitude. Informants suggested:
“…having knowledge based on the criteria.”
“…the selection criteria should consider knowledge, critical thinking ability, and aptitude which may be difficult to measure.”
Local resident refers to local applicants who can work as a nurse to serve in the local area. Informants stated that students:
be “…a resident in the area, and through the experience training in specialized course,”
“…have to focus on the kindness of people in the countryside for this group has fewer opportunities to get health service than people in town.”
Science and art backgrounds are both important. They further stated that BCNS:“…allows students from both science and arts high schools to study.” 
Community participation in the admission of nursing students is discussed, with suggestions such as pre-admission camp. They stated that: 
“…community should participate in the selection process, and nursing students should attend a training camp in patient care as the pre-selection criteria.” 
“…pass the minimum criteria with community participation in the selection process, for which high grades are not necessary. The community will help select the candidate and support scholarships which will attract the nurse to stay in the community after graduating, and solve the problem of urban concentration.”
“…the nursing curriculum should add people with other bachelor’s degrees from the community who have more maturity with responsibility for self and society.”
A service mind was described as
“…nurses must be really kind to the patients without discrimination, do not have money as a goal…”
“…love to be a nurse, love being a nursing professional, be patient and care for others.”
Teaching and Learning
The curriculum development needs to be up-to-date and support holistic learning and empathy through teaching theory, practicing with multidisciplinary teams, and supporting community links. Teaching and learning management were seen as necessary for successful curriculum implementation. Teaching and learning is composed of 8 elements: updated curriculum, empathy, student-centered learning, moral theory and practice integration, case-based study, critical thinking, multidisciplinary work, and love of the nursing profession.
Updated curriculum
Informants felt that the curriculum should be updated so that it is modern and filled with holistic nursing care. The informant stated that: 
“The course needs to be good and modern and should add humanized mind.”
Student-centered learning
Student centered learning has been identified as a central target of curriculum development. Informants said:
"…the learning process should focus on the student which creates fun, intimate, informal relationships, and a safe space to share ideas."
"In teaching and learning, the instructor must add joy during learning. Do not use too many rules and the instructor must be a role model, guide; do not focus on lecture
Theory and practice with moral integration
Theory and practice with moral integration, both in the theory part and clinical part, are needed. Informants shared that:
“…learning …development of moral principles according to the Buddhist doctrine.”
“…project-based leaning helps the students learn the management of money, human relationships and resource sharing.”
Case-based study. Case-based study should be used to provide understanding of real life situations as part of curriculum development. Informants stated that: 
“… case study provided more experience and understanding through real life practice.”
“…learning through case study facilitated the understanding more on the patient.”
“…teaching through teamwork, practicing taking turns on team leader practice.”
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is discussed as learning outcome results of using different teaching methods. The key informants exchanged their different ideas as:
“…using project-based learning [PBL], in conferences, instructors will have techniques to teach how to discuss and make suggestions. Analysis thinking is the highlight of college.”
“…evaluation should measure the thinking, training. Do not measure the knowledge or recall,…address the formative feedback for learners to develop themselves on transformative learning.”
Multidisciplinary work
Multidisciplinary work was discussed. The discussion focused on the steps needed in teaching about nursing. The key informants said:
“…the teaching and learning should focus on multidisciplinary work. Start with some parts or some of the subjects first.”
“The teaching of nursing management should include multidisciplinary work by starting with some parts of the subject.”
“..training with network partners in our own professions and other professions to learn how to work in public.”
“…teaching and learning teamwork skills and taking turns to practice team leader competency.”
“…training by network partners in our own professions, and other related professions were promoting learning of how to work in public.”
Love of the nursing profession
Love of the nursing profession was discussed as a goal of teaching that encourages the love of a career in nursing. An informant stated that:
“…teach them to love their profession, be responsible for nurse assigned task.”
Course and Curriculum
The course and curriculum in nursing was embraced in two groups: course content and degree extension courses.
Course content
Course content was found to have seven subgroups: idea triggers, main idea, infectious control, emergency special code, real situation experience, problem-based learning, and self-development.
Idea triggers
Idea triggers were discussed as relating to content and teaching methods for new students. The key informants expressed the thoughts as:
“New students like simple, quick tools rather than wanting to know a related story. So content and teaching methods need to be modified”
Main idea
The main idea should be precisely presented without too much unnecessary detail. Moreover, instructors should be role models of self-directed learning and have broad visions in ethics and issues in real-world health services. The key informants stated that:
“… service site gave both memorable content and real atmosphere.”
“Teaching in the 21st century must train the student to use self- directed learning.”
“The instructor must be a role model, teaching with many aspects’ integration such as service context with professional ethics.”
Infections control
Infectious control was discussed in terms of nursing management for prevention and control of infection through medical equipment. Key informants emphasized
“… the management of sterilization of medical equipment, infection control.”
Real situation experience
Real situation experience was proposed to have content about daily living in the community, culture and real healthcare settings, which differ from hospital settings. Therefore, graduates will be able to adjust to work after graduation. The key informants suggested:
“…maybe content about the community’s way of life, focusing on culture. Instructor s must be linked to the community to practice holistic nursing.”
“Practice more in real situations, early exposure to real experience.”
“…touch the truth in learning site, work with network partners, look at the problem in the big picture, self -study, learn how to learn, more than spoon feeding.”
“…learning the real situation… bring a lawsuit in which nurses talked to a patient badly. Then discuss and learn how to communicate well.”
Problem based
Problem based was the teaching method that promotes critical thinking and problem solving during clinical or community practices. The key informants said that:
“…addressed on case conference which can exercise discussion and critical thinking, instructor and friend suggestions will add knowledge, might be time consuming process, which is better than only routine work.”
“…community coaching starts in real life by facing the problem, then solving the problem, later bringing the case to the conference where students will gain problem solving and co-ordination skills.”
Self- development
Self- development was suggested as part of computer literacy for nursing students. Key informants suggestions included:
“…add technology to the preparation for data presentation, such as diagrams, because it is commonly used in real work. It is a chance for students to learn the public health data system related to nursing jobs.”
“Encourage students to pursue professional and personal development.”
“Each learning year’s capacity should be identified. There is a performance ladder. In the 1st year, instructors will determine what students’ core competencies are. In the first part of the year, this will act as a base for thinking systematically and setting up friendships…We should expect more from 2nd year students.”
“…General education courses in chemistry, physics, and biology can be applied in nursing probably linked to the 2nd year and 3rd year.”
Degree-extension courses
Degree extension course refers to additional new courses in specific nursing areas. An informant stated that: "in the future, we might need more new, specialized courses which are required by some specific areas.
Instructor Tasks
Instructors should apply student-centered teaching concepts. The instructors’ tasks include five elements: elicit student ideas, provide opportunities to learn, support infrastructure, support technology use, and extracurricular activities to promote being good people.
Elicit student idea
Eliciting student ideas engages and motivates learners in their studies. The informants stated that
“Instructors must motivate students how to learn rather that teaching all the content.”
“…Instructors must coach and facilitate, sharing ideas with the students.”
“…Instructors need to find methods that foster learning, like using the learning technique of the Buddhist concept of Su Ji Pu Li (listening, thinking, questioning, and writing).”
Provide opportunities to learn
Instructors should provide opportunities for students to learn about various issues with other professions. Key informants said that
“…Instructors must provide the chance for students to practice more, early exposure to real situations, and to interact with other professionals and patients.”
Infrastructure support
Instructors should provide infrastructure support in the classroom and learning tools for achieving multiple skills. The classroom should be conducive to the development of multiple skills and learning support should include updated tools and suit the learner. A key informant provided details saying,
“Learning in the new century should focus on a variety of skill development. The classroom should be a flat floor, conducive to group activities.”
Technology support
Technology support was discussed as it relates to readiness and availability of education technology and computer staff onsite. The informants pointed out that:
“…occasional booking and the coordination of staff to prepare audiovisual equipment for events is not convenient and a barrier to instructor creativity in organizing activities.”
“…higher technology should have handout support, such as the training robots, which should have videos that show all their function, which will good for the 21st-century student.”
Extracurricular activities
Extracurricular activities were discussed as a means to promote being a good person. Key informants reflected that:
“…The volunteers’ spirit came from the activities and promoted being a good person.”
“…can apply knowledge learning from college to social life and professional.”
Discussion
Perspectives of Stakeholders on the Desired Characteristics of Nursing School Graduates
This study reflects society’s needs in the future, including: 1) having the knowledge and practical quality standards; 2) communicating and using the English language well; and 3) having a balanced life and knowing the world. Future societies require nurses with knowledge and quality practice, who have passed quality standards test. This is because nursing work affects the life and health of human beings. The results of the research are supported by the direction of professional organizations that define the characteristics of nurses in the next decade, saying that nurses must have skill specialization in nursing practice, have academic ability, and can use judgment and decision-making to solve health problems (Nursing Council, 2008). Nurses need to communicate well. Miscommunication was problematic and led to prosecutions in a variety of cases involving nursing.
Professional nurses provide health services to both healthy and unwell people of all ages and integrate work with multidisciplinary teams and people of all levels. Thus, communication for good understanding is important for quality health services. This is consistent with a research report that states graduates need to have skills in their work, be able to work with others, and have skills in using language for communication (Chidnayee et al., 2014).
In addition to communicating using the Thai language easily and effectively at work, nurses also need English communication skills to enhance their abilities to perform nursing care in a borderless world. Nurses have to balance life and know about the world because nurses work to take care of all age groups, either healthy or unwell, leaning to a large workload and fatigue affecting personal and family lives. Research showed that nurses need to know how to balance their lives and work to be efficient and happy at work (Thipvatee et al., 2017).
Perspectives of Stakeholders in the Nursing Curriculum Development
Selecting students requires emphasizing the importance of people in the area. The selection system allows the community to participate and gives more opportunities for local or arts high school students. The basic knowledge should meet the entrance criteria. There is a study that found that the cumulative GPA was significantly correlated with the academic achievement of nursing students (Khemapech, 2015).
The teaching process focused on learning from real-life exposure and integrated learning. Learning through a project activity was beneficial to learning because the activity covered the integration of all the knowledge in the work, by learning about real situations, in a context related to the patient or community, and demand or need analysis. Searching for knowledge, finding a co-worker network, accessing resources, working with others, communication, leadership training and followers, presentation, learning and working development were congruent with the new-generation learning approach through the project activity (project-based learning) for effective learning (Panich, 2012), and assessment of thinking and self-improvement rather than assessment of knowledge.
The global community is rapidly changing, in particular in communication technology, which is bringing about new transformations of data. This caused a phenomenon called “Information flow/flood/bomb blast.” Nurses must have lifelong learning skills and apply holistic knowledge in their work (Siripan, 2013). Skills in pursuing lifelong learning and media literacy were essential and nursing students should critically analyze the reliability of information. Instructors cannot bring all the knowledge. Thus, the instructor must spark student ideas, create curiosity, and encourage students to become self-answerers. The classroom floor should be flat to facilitate a variety of learning activities. Teaching materials must be up-to-date and convenient to cultivate lifelong learning.
Suggestions
The study of the characteristics of nursing graduates and curriculum development from the perspective of the stakeholders that is from the alumni users (supervisors and colleagues), alumni, and alumni’s instructors showed the important guidelines for the selection of student candidates, instructional management and outcomes of nursing characteristics in the future. The results showed the curriculum developments and educational management of new student selection that should consider basic knowledge and involve the local people and more community participation. Teaching must focus on training in real situations and work integration by encouraging self-learning and lifelong learning among the students in order to keep up with academic growth and rapid social changes.
Biographical Notes
Prapai KITTIBOONTHAWAL, MPH, RN is a lecturer in the Department of Community health Nursing, Boromarajonani College of Nursing Saraburi. Her research interests include community health, and reflective teaching method.
She can be reached at Boromarajonani College of Nursing Saraburi, 18/64 Tessabarn 4 Rd., Muang District, Saraburi 18000, Thailand or by email at prapai@bcns.ac.th.
Wareewan SIRIWANIJ, PhD. is a lecturer, Clinical Nurse teacher of Maternal and Child Nursing, Midwifery at Department of Maternal and Child nursing. Her research interests include Maternal and Child Health & Nursing, nurse education, woman health, reflection skill, transformative learning skill, and critical thinking skill.
She can be reached at Praboromarajchanok Institute, for Health Workforce Development, Ministry of Public Health, 8th Floor, Block 4, Permanent Secretary Office Building, Tiwanon Rd., Muang District, Nonthaburi, 11000, Thailand or by email at wareewan@pi.ac.th or wareewan@hotmail.com
Kanyarat UBOLWAN, PhD., RN, is a lecturer in the Department of Adult and Elderly Nursing, Boromarajonani College of Nursing College Saraburi. Her research interests include fall, chronic disease, and health promotion of older population.
She can be reached at Boromarajonani College of Nursing Saraburi, 18/64 Tessabarn 4 Rd., Muang District, Saraburi 18000, Thailand or by email at kanyarat @bcns.ac.th.
Munthana MANEECHOT, MSN, RN is a lecturer in the Department of Maternal and Newborn Nursing and Midwifery, Boromarajonani College of Nursing Saraburi. Her research interests include sexual health, teenage pregnancy, sexual risk behavior in adolescent, and the development of active learning, the health promotion in maternal and newborn.
She can be reached at Boromarajonani College of Nursing Saraburi, 18/64 Tessabarn 4 Rd., Muang District, Saraburi 18000, Thailand or by email at munthana@bcns.ac.th.